Seeing in the Dark - Nighttime’s Potential in Urban Innovation
Header-Image Credit: NASA, ESA, H. Bond (STScI) and M. Barstow (University of Leicester)
Update June 2025
After our WUF12 panel “24-Hour Cities Against Climate Change”, I was in touch with the editors of Nature Cities. In June 2025, Nature Cities published its Volume 2, Issue 6, “Cities after dark”, which also features my I and the City piece “My city never sleeps”. The article picks up several of the ideas discussed in this post.1
This is a follow-up to my last blog entry “My personal Night-Shift: Finding Out about the Importance of a Topic”, where I outlined my personal journey towards understanding the significance of the night and culture in urban development.
Introduction: The Night - The Forgotten Time in City Development
I spend most of my working time on projects on sustainable city development. When I bring up the topic of the urban night in this professional context, I often encounter similar reactions: Either a grin or a confused look. A reaction that seems to ask, “this is a fun topic, but what exactly is the connection to what we’re doing here?“. Being in a professional context, I have the impression people want talk about professional topics. And these reactions suggest a perception that the night is not one of them; maybe a topic more for leisure, relaxation or socialising and distinct from ‘serious’ urban issues.2
Much like in my previous blogpost, I want to challenge this notion with a bold claim: What if the after-work hours are precisely when we can best address some of the most pressing urban challenges?3
With insights from my colleagues at Fraunhofer, vibelab, and beyond, I’ve shaped my thoughts around this idea. This blog post will explore those around three core thoughts:
-
To tackle the global challenges we face, we need creativity and the cognitive ability to break away from old patterns - qualities that are often more accessible in the after working hours, when we can easier move away from the constraints of formal professional settings3.
-
The underlying reasons sustainable/green city development and cultural engagement/nightlife aren’t already central to mainstream urban planning are similar: Difficulties in attributing the benefits they provide for society as a whole in economic terms.4 5 6 If the underlying reasons why they are overlooked resemble each other, overlaps should be able to be identified; and consequently ameliorating one sphere could inform and enhance the other simultaneously. Therefore, synergies between the two should exist and could be actively developed and used.
-
Cosequently, could it be, that the disconnect between after-work life and the sustainable city development agenda is a major factor of what’s slowing our progress towards major urban transitions?7
The Night: Why Is It Underrepresented?
The figure below summarises the key points drawn from the publications I read in the process of getting acquainted with the overall topic of nighttime socioeconomics and nighttime ecology. The mentioned arguments made a lasting impression on me and I tried summarising their essence in the following (see footnotes)8.
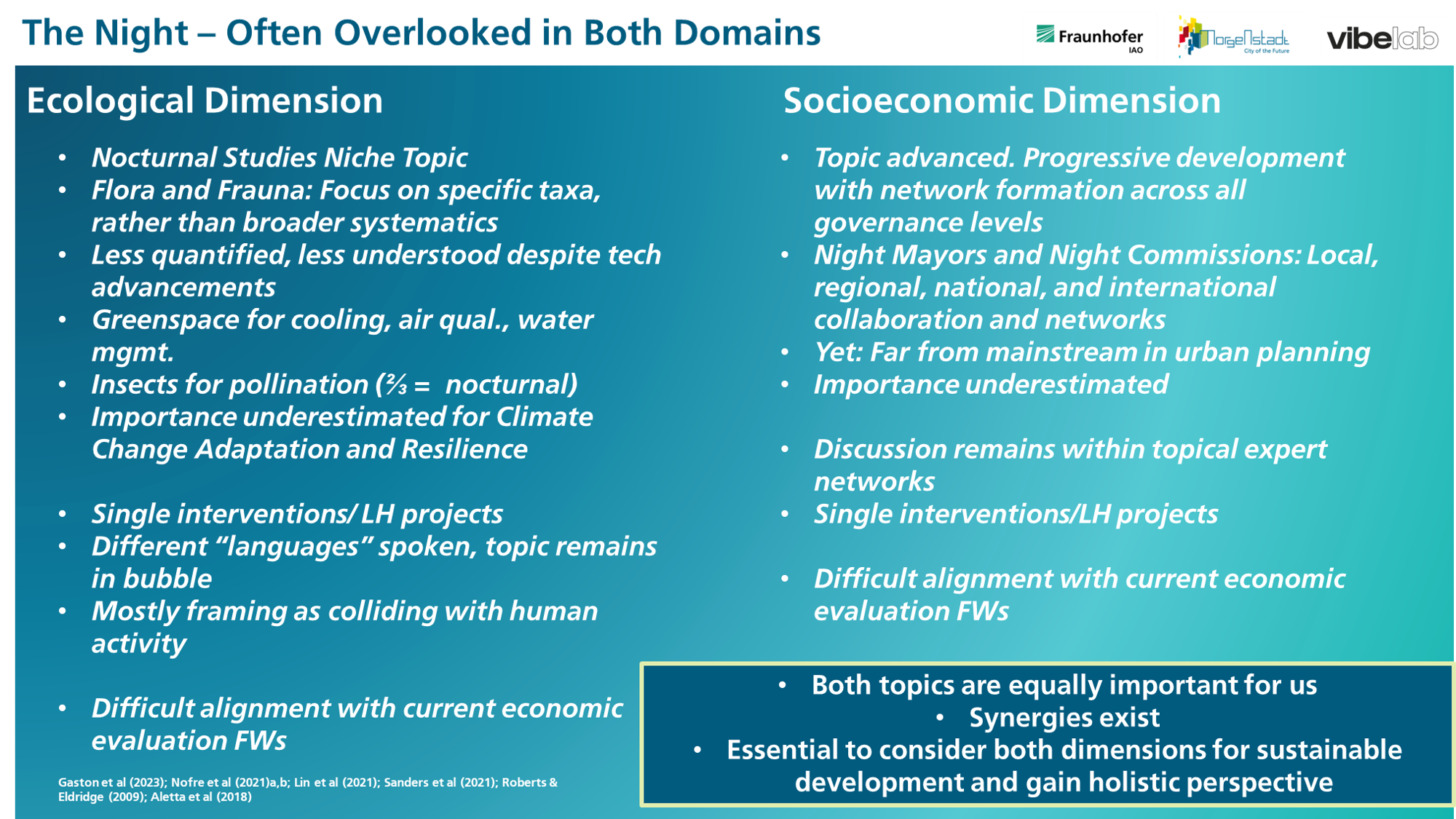 Nocturnal Ecology and Nocturnal Socioeconomics opposed
Nocturnal Ecology and Nocturnal Socioeconomics opposed
What literature says:
Societal Perspective2 7 9 10 : What struck me most was a frequently described and seemingly common pattern among urban planners, policymakers, and researchers alike: Most prefer daytime for their professional activities, often neglecting night-time considerations once their workday ends.
Ecological Perspective5 10 11 6 12: Interestingly, to me, most of the key observations in articles from this context could be applied to both ecological and socioeconomic aspects of nighttime. I added the possible relevance for the socioeconomic sector in brackets behind the original arguments I took from my ecological readings:
- Nighttime plays a critical role in ecological balance, analogous to its importance during daytime, yet it remains a niche area of research. (Undoubtly this is true for the societal sphere as well. I’d argue (night-)culture plays a critical role in societal balance. In the societal sphere there is a large advocacy movement on all levels of governance. Yet the topic itself is still far from being part of mainstream city development).
- Its significance is frequently underestimated, leading to its underrepresentation in ecological considerations (…and in urban planning discussions).
- The preference among ecologists to work during daytime contributes to the scarcity of focus on nocturnal studies. (Just like their counterparts in urban planning).
The Challenge with Economics and Economic Metrics
Like in any sector, economic considerations are a driving factor (if not THE driving factor) cities are fundamentally influenced by. Like the economy as a whole, cities aim to create an economically sound and thriving environment for their inhabitants and economic actors. Which itself ultimately underlies all subsequent activities. However, this economic focus often is a difficult fit with both cultural and ecological initiatives. Let me give you two illustrative examples:
Socioeconomic Aspects: Prevailing Informality10
- During almost all of my side gigs while studying and working in hospitality/nightlife, I received my wage payment in cash. These transactions never made it into official economic statistics or tax-related key performance indicators (KPIs). This situation reflects a broader reality: A significant portion of nighttime economy is informally managed, often out of necessity due to stringent regulations. It is therefore not fully represented in financial KPIs of a city. Simply increasing enforcement, such as deploying more tax officers, is not a practical solution.
Ecological Considerations: The Parking Spot Problem11 6 12
- Think about the lifecycle of a typical urban parking spot. Initially, there’s a one-time investment to pave the area. Install a parking meter, and the city enjoys a steady inflow of cash from users. Favourable budgeting no-brainer!
- Now, replace that parking spot with a public garden or a tree. While the initial costs might be similar for removing asphalt and planting, the ongoing expenses for maintenance like gardening and watering present a less appealing economic case under traditional city budgeting models13. Despite numerous studies showing the financial and social benefits of greener urban spaces, widespread adoption remains limited without public intervention.
In a Nutshell: Qualitative Aspects outweigh Monetary Benefits
There’s a reason, why the above mentioned economic metrics are ever so popular: Simplicity. City administrators, planners, politicians, and executives often operate under tight deadlines, needing to make swift but far-reaching decisions. They rely on clear, quantitative data to inform and justify their decisions (in the best case displayed (visually on e.g. dashboards)9).
Integrating new frameworks of calculus, that integrate e.g. the environment6, requires extra effort: Data collection, harmonisation, staff training, IT infrastructure etc. So, why not stick with simpler, straightforward metrics?
But to me, could not the viewpoint and angle be a difficult fit from a start:
What if the non-monetary benefits that both culture and nature bring to urban environments significantly outweigh their economic benefits? Imagine the value of spending time with friends under a leafy tree outside a charming café, or the lasting memories created from a night out at a lively bar or club. How do we quantify these experiences? For those of us reflecting on our youth, how significant are these memories for you?
Yet, either way you turn it: In the real world as of now, there’s no escaping economic metrics. They underlie all subsequent activities. Even if economic benefits are not the target of the things you try to set in motion through cultural and green city development.
But change comes gradually. And we may try being a part of it :)…
The Missing Link
Through my experiences in both sustainability and socioeconomic sectors of city development, including my role at the Nighttime Innovation Network at Fraunhofer since 2022, I have observed a critical gap in how these two spheres intersect and influence city planning. Let me give you my main observations in concise bullet points:
- Large-Scale Integration Lacking - There is a notable absence of a systematic, large-scale linkage between ecological sustainability and the socioeconomic aspects of the after-work time. Each sphere often attempts to address problems related to sustainability based on its own understanding, without substantial cross-disciplinary collaboration. The link yet has to be made in an systematic way on large scale (e.g. in the multilateral sustainable city development my employer Fraunhofer and the Department of Urban Systems Engineering pursues)14.
-
Small-Scale Conflict Mediation Dominates - In the realm of nightlife and socioeconomics, the focus often remains on resolving immediate, localised conflicts (e.g., between a bar, a restaurant and its neighbourhood) rather than fostering broader synergies that could benefit the city as a whole. Again, because the link mentioned above is seldom systematically made.
-
Focus on Conflict Resolving rather than on Synergies - In the topic, discussions often circulate around human activity and its collision with the needs of ecology. Focussing on the conflicts can lead to a further mismatch between needs of ecology and current urban and economic realities. Finding common ground gets difficult and discussions lengthy. Realigning the focus on the development of synergies could possibly have a greater impact and positive entanglement of societal and ecological advocates. An example here could be the ‘light pollution’ debate 15 , which is one of the center discourses in the field. It is a crucial topic to address. Yet, I think it is a term that inherently suggests conflict rather than cooperation between human needs and environmental considerations16. Put very simply: Nature wants it dark, humans want it illuminated. It requires a lot of negiotiation and education to change this (please see footnotes17 18 19). Also within each sphere the prevailing discourses focus on conflict resolution rather than creation of synergies. 2 10 15
The Benefits - What Do Culture and Ecology Offer, Why Are They Both Vital for Cities?
Both culture and ecology significantly enrich urban life, providing a host of amenities that enhance the liveability and appeal of cities4. These two spheres are fundamental to the attractiveness of urban areas, influencing not only the residents and visitors but also playing a crucial role in where people choose to reside, especially in Western societies.
Fair enough, but here I want to make the bold and (to me) straightforward assumption, that culture and ecology both are at the very core of why some cities continue to thrive while others descend:
- What happens if a city is not safe/stable to live in? Yes, easy answer: If they can, People will try moving somewhere else.
- What happens if a city is not attractive to live in? Yes, easy answer: If they can, people will try moving somewhere else.20
- What happens if a city is not healthy for its inhabitants or for them to raise their kids? Yes, easy answer: If they can, people will try moving somewhere else.20
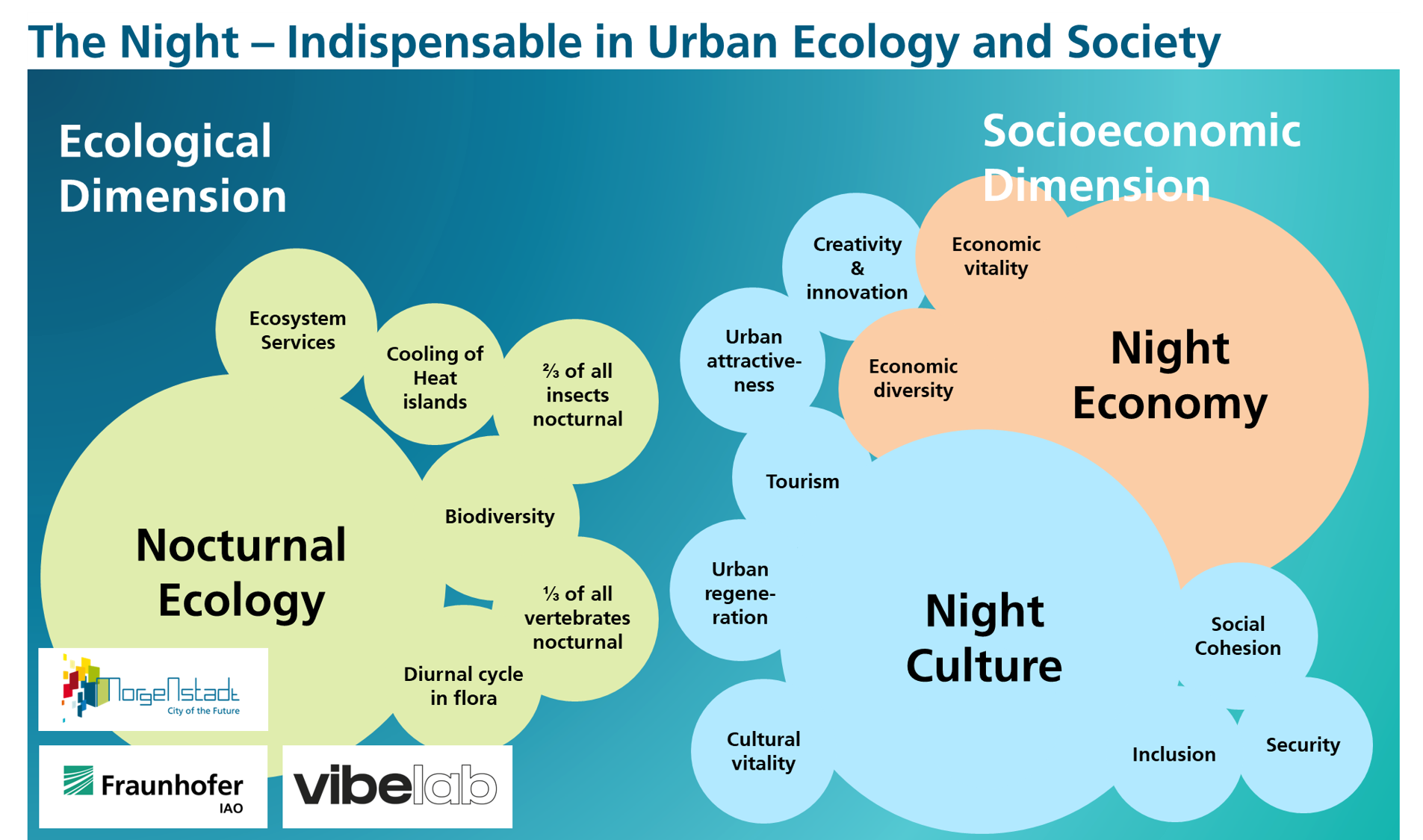 Ecological and Socioeconomic Dimensions of the Urban Night Side-by-Side
Ecological and Socioeconomic Dimensions of the Urban Night Side-by-Side
For some of the mentioned characteristics both do not only contribute to attractiveness, which is a more or less optional urban development area, but also to vital urban functions4 that are at the core of what a city needs to offer to its citizens: E.g. safety and economic vitality or cooling and water management. Without those, a city will only poorly function.
The Figure above hightlights the individual role of socioeconomics and ecology within the urban system … What could be possible if we try bridging and synergising both?
Finding Ways Forward - Finding the Synergies
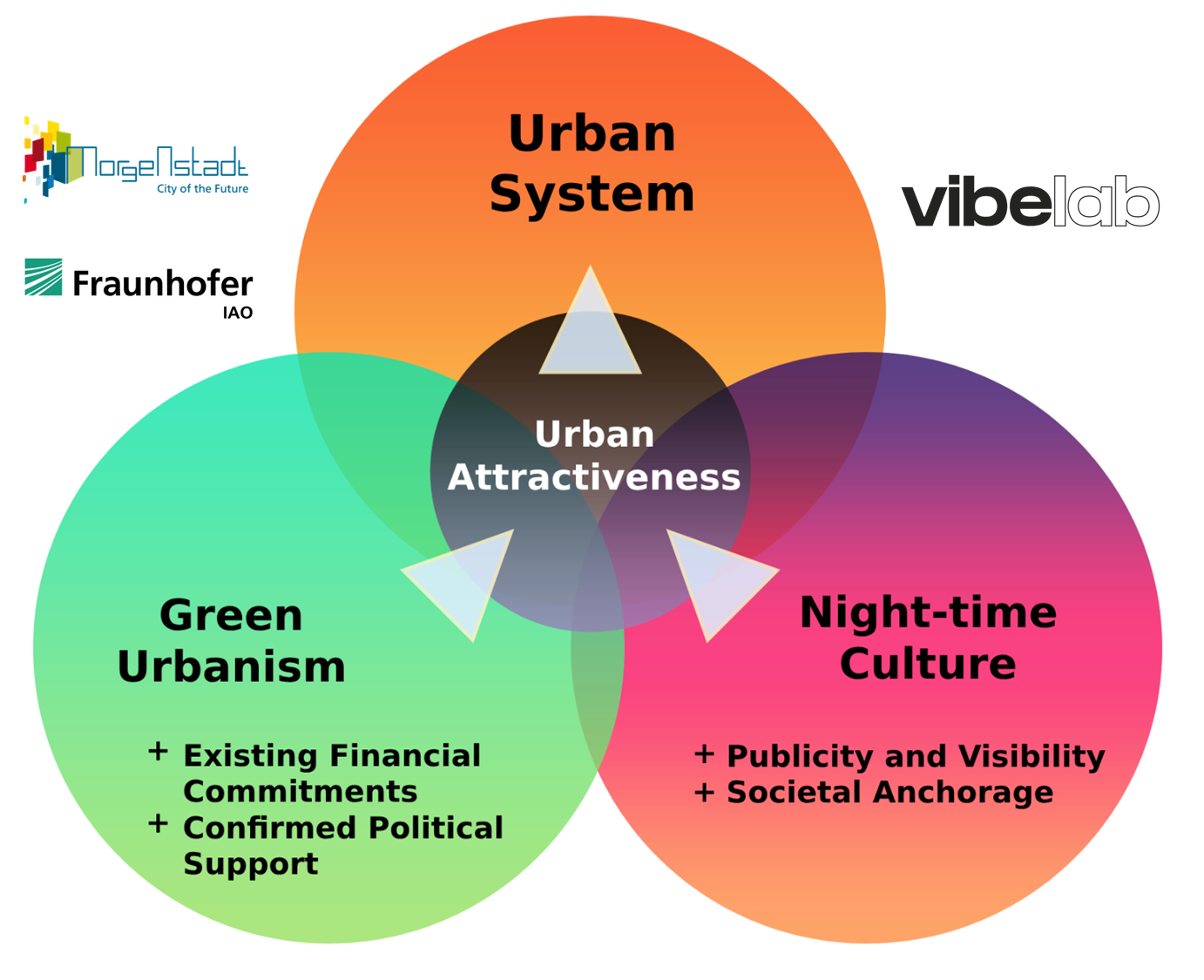 Proposition: Green Urbanism and Night-Culture in Synergy to enhance the Urban System as a whole.
Proposition: Green Urbanism and Night-Culture in Synergy to enhance the Urban System as a whole.
Okay, good we know now…. But what do?!
To me, we should try finding an easy beginning. A beginning where we most likely will face little confrontation but enable those much-spoken synergies in a visible way. The link needs to be easy for everyone to understand the connections and the benefits what thinking about the “other sphere” can provide. Then over time, we may add the more delicate topics that maybe require more discussion and negotiation.
Together with Lutz Leichsenring from Vibelab, I, through my employer Fraunhofer IAO and the Department of Urban Systems Engineering started this process. Among other conferences and thanks to Lutz and Vibelab, I could take part in the ‘South by Southwest Conference and Festival - SXSW’ and the panel “The Transformation of Nightlife for a Sustainable Tomorrow”. This was the onset of our common considerations and since then we meet every couple of weeks to inspire us and to push things forward.
Push Things to Where?!
-
One of the easiest links you may find bridging those spheres is Green Soundproofing. I wrote an article on our institute’s blog about this and soon afterwards a couple (!) of German cities reached out and showed their interest. The thought is easy: We spend so much on greening our cities, why not include nighttime culture and get double the benefit?
-
And I’d say this is exactly the way to go: Find and make use of the easy links. Make it visible. Make it bold. But above all make it easy to participate.
-
Well, listen closely: Coming to your city soon. Vibelab and Fraunhofer will make it happen :)!
… We will provdide a detailed description of our Green Soundproofing concept, the other initiative in the making (“Urban Systems Network Smart City @ Night”) and other practical ideas in the upcoming blogpost. Open-Source and free, just like both night and nature should be :)…
Epilogue: Seeing in the Dark - Nighttime’s Potential in Urban Innovation
Reflecting on why night-time issues remain underrepresented in urban planning reinforces my belief in the need for integrating efforts across both cultural and ecological dimensions. Ultimately, strategies that promote sustainable or green city development can be inherently beneficial for cultural and socioeconomic initiatives and vice versa.
A couple of weeks ago, I watched Jim Jarmusch’s “Night on Earth”, where a taxi driver picks up a blind passenger21. The dialogue goes like this:
Taxi Driver: “It must be really hard to be blind, you’re unable to do so many things.”
Blind Woman: “Listen, jerk, I can do anything you can and a lot of things you’ll never do. I’m blind, that’s all.”
Taxi Driver: “You can’t drive a car, for example.”
Blind Woman: “And you can?”
The joke is, that the driver soon has an accident after this talk.
To me, this dialogue set in motion a stream of thought. I see that this could be understood as metaphor for the topic of this blog post. Urban development has perhaps been ‘blind’ to the full potential night and culture can offer. With the urban re-greening initiatives underway but in a rather ambient pace, also urban development may does not ‘see’ the full beneficial value of re-naturing cities.
Earlier this year, I attended the “Blind Date with Stuttgart” exhibition, an event that transformed participants’ understanding of their environment by navigating a replica of common places in Stuttgart in complete darkness. We were guided by blind individuals. It was unimaginable how difficult I found it to find my way. I and the other participants had to rely on our other senses - feeling, hearing and scenting.
And this is where I see a possible connection to the topic at hand:
City development, to grasp all possible benefits, disbenefits and pathways, requires a full spectrum of senses. Perhaps it’s not about ‘making cities ‘see’’ the night or about ‘taking cities’ ‘blindness’’ towards the incredible potential of culture and greening through conventional pathways, by e.g. adapting conventionally used economic metrics, coming up with new KPIs or merging existing ones into more sophisticated units. We tried this with extensive sustainable urban development programmes in the past decades.
Maybe it is more about developing a new ‘sense’ or readjusting towards other, maybe forgotten ‘senses’ for how the urban environment functions around the clock.
Could developing the bespoken synergies be a way? Let us find out. And if you want, let us find out together.
A special thank you to Lutz for revising this text.
… Be in touch: niklas.effenberger@iao.fraunhofer.de
This post has been published on under the same title on Nighttime.org
-
Effenberger, N. (2025). My city never sleeps. Nature Cities, 2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44284-025-00244-8 ↩
-
Relevant are several articles of the 2019 Special Issue “Temporal Justice in the City. Concepts and Perspectives for Planning Practice” published by the Academy for Territorial Development and Henckel, Dietrich; Kramer, Caroline Eds.; helped me by a lot. Link. ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
In line of the idea here. A great read that proposes a radical shift towards a so called ‘consciousness culture’. To foster a future marked by compassion and self-respect . Written by philosopher and neuroscientist Thomas Metzinger (2023): Bewusstseinskultur: Spiritualität, intellektuelle Redlichkeit und die planetare Krise. Berlin Verlag. EAN 978-3-8270-1488-7 ↩ ↩2
-
Gehl, J. (2010). Cities for People. Island Press. Groundbreaking and visionary book. Gehl’s principles for designing human-centred cities align with the ideas presented here and how urban design can enhance both ecological and social spaces. ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
A classic when it comes to Nature-Based Solutions: Kabisch, N., Korn, H., Stadler, J., & Bonn, A. (Eds.). (2017). Nature-Based Solutions to Climate Change Adaptation in Urban Areas: Linkages Between Science, Policy, and Practice (1st ed.). Springer Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56091-5 ↩ ↩2
-
See: Chausson A et al. (2023) Going beyond market-based mechanisms to finance nature-based solutions and foster sustainable futures. PLOS Clim 2(4): e0000169 doi.org/10.1371/journal.pclm.0000169. And Brears, R. C. (2022). Financing Nature-Based Solutions: Exploring Public, Private, and Blended Finance Models and Case Studies (1st ed.). Palgrave Macmillan Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93325-8. ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
Görtler, M. (2015). Zeitforschung aus sozial-ökologischer Perspektive. Ökologisches Wirtschaften - Fachzeitschrift, 30(4), 17–18. https://doi.org/10.14512/OEW300417. ↩ ↩2
-
Please note that this summary is not exhaustive neither in regard to available literature nor in regard to content of the individual publications. ↩
-
Cool article on how long the idea of having a dashboard to grasp ongoings in a city is out there: Shannon Mattern, “Mission Control: A History of the Urban Dashboard,” Places Journal, March 2015. https://doi.org/10.22269/150309. ↩ ↩2
-
Selection of readings: Jordi Nofre: “The Urban Ecological Transition and the Future of Europe’s Nightlife Industry” (2023),doi: 10.1080/16078055.2022.2162112; Kevin J. Gaston: “The Nocturnal Problem Revisited” (2019), doi: 10.1086/702250 and “Anthropogenic Changes to the Nighttime Environment” (2023), doi: 10.1093/biosci/biad017; Acuto, Michele, et al. Managing Cities at Night: A Practitioner Guide to the Urban Governance of the Night-Time Economy. 1st ed., Bristol University Press, 2022. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctv22jnkcq. ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
A city planner from Eindhoven told me this illustrative example during the research for my Master Thesis. Until today, to me this is one of the clearest explanations on how economic metrics sometimes fail for common goods like greenery. P.s.: Elionor Ostrom received the Nobel Prize for describing this already in 2009. See her [Lecture here]https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/economic-sciences/2009/ostrom/lecture/). ↩ ↩2
-
Good read: “The hidden force that shapes everything around us: Parking.”” Marin Cogan in Vox, May 2023. ↩ ↩2
-
See election poster Christian Democrats Stuttgart: “No to the Loss of Parking Spaces!”, Stuttgart, Germany 2024; On their Facebook Page ↩
-
And I’m confident that Fraunhofer teaming up with vibelab can do the job :)! ↩
-
Maybe it is so prominent because it is one of the clearest links when thinking about a natural night (dark) and nightly human activity (illuminated). Notably, research indicates that reducing urban lighting does not necessarily correlate with increased crime rates. Yet a fear of removing lighting persists, deeply ingrained in human and societal concerns about darkness. Since this is deeply engrained, it is certainly not easy convincing people otherwise, even the most rational beings. Interesting and controversially discussed read: Zhong CB, Bohns VK, Gino F. Good lamps are the best police: darkness increases dishonesty and self-interested behavior. Psychol Sci. 2010 Mar;21(3):311-4. doi: 10.1177/0956797609360754. ↩ ↩2
-
Artificial light paved the way for lively urban neighborhoods after dark, see e.g. this book on how London’s nightlife evolved and how it is (for philisophists) to take a night stroll: Beaumont, M. (2016). Nightwalking: A Nocturnal History of London. Verso. Or how city-lighting changed everything from work to pleasure: Schlör, Joachim. Nights in the Big City: Paris, Berlin, London 1840-1930. Reaktion Books, 1998. ↩
-
Good watch/reads: Sabine Hossenfelder Backreaction March 2022 - “Is light pollution a real problem?”. And “Illuminating the Effects of Light Pollution.”, The New York Times, Apr 2016 (paywall). ↩
-
Studies show that significant contributions to light pollution often occur in peripheral areas, such as parking lots and suburban streets, rather than dense urban centrers. While there are numerous successful pilot projects around the world that address light pollution with innovative engineering solutions, they rarely advance beyond the pilot stage due to high costs and complexity, limiting their broader adoption. See1 e.g. unexpected sources of light pollution like a massive greenhouse in Maine or oil fields in N-Dakota: “Mysterious Light Sources”, Altair Space (2 March 2020). See2, streetlights are not the primary contributors: Gill, Victoria. “Light pollution’s wasted energy seen from space.” BBC (Oct 2020). See3, the engineering solution. To me looking a bit like taken out of a horror movie: Bat-friendly lighting in Gladsaxe, Denmark. Afry enginnering. n.d. ↩
-
Debates on Lighting and Safety: I recall a particularly telling debate between an ecologist experienced in lighting issues and a nighttime economy advocate. The discussion revolved around the need to reduce lighting to prevent biodiversity loss versus the need to avoid creating spaces that feel unsafe. Such discussions highlight the difficulty in finding ‘middle’ ground where ecological and human needs align, suggesting that more dialogue, work and dedication are necessary to bridge these viewpoints. When you think about the beginning of why streets were lit up: It was street lighting that enabled nocturnal life in the cities in the first place. ↩
-
Florida, R. (2002). The Rise of the Creative Class. Basic Books. ↩ ↩2
-
Taxi driver played by Isaach de Bankolé and blind woman played by Béatrice Dalle. ↩
